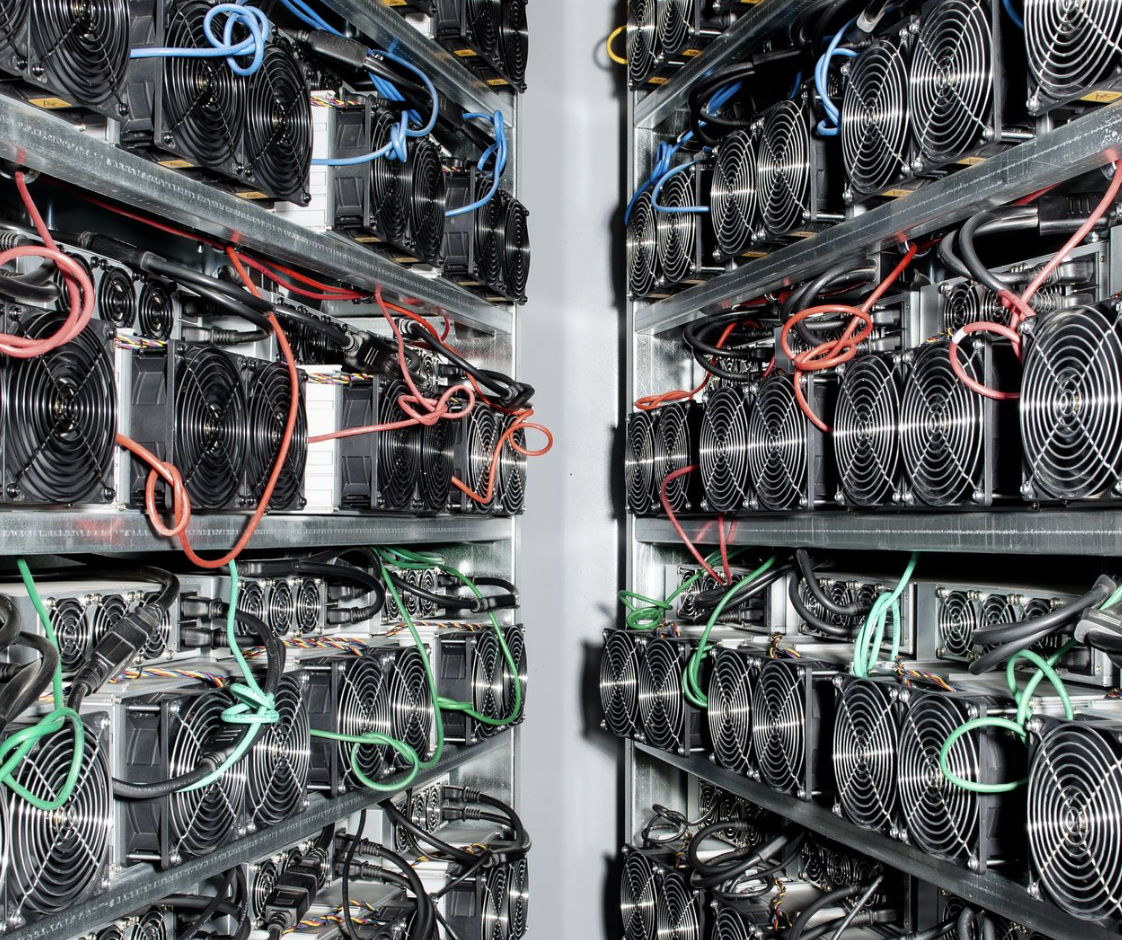
Introduction to Crypto Mining
Understanding Crypto Mining Cryptocurrency mining, often referred to simply as "crypto mining," is the process by which new digital coins are introduced into circulation, and transactions are added to a blockchain ledger. This decentralized and highly technical process ensures the security and verification of cryptocurrency transactions without the need for a central authority. How Does Crypto Mining Work? The Basics Crypto mining involves solving complex mathematical problems using powerful computers. When a miner successfully solves one of these problems, they validate transactions and add them to the blockchain. In return for their efforts, miners are rewarded with newly minted cryptocurrency coins. The Mining Process Transaction Verification: Miners compile a list of transactions into a block. Problem Solving: They solve a cryptographic puzzle, which is computationally intensive. Block Addition: The first miner to solve the puzzle broadcasts the solution to the network. Reward: If the solution is correct, the block is added to the blockchain, and the miner receives a reward in cryptocurrency. Types of Mining Proof of Work (PoW) Proof of Work (PoW) is the original consensus algorithm in the blockchain ecosystem. It requires miners to solve complex mathematical problems to validate transactions and create new blocks. Bitcoin, the first cryptocurrency, uses PoW. Proof of Stake (PoS) In contrast, Proof of Stake (PoS) relies on validators who hold and stake a certain amount of cryptocurrency. Validators are chosen to create new blocks based on the number of coins they hold and are willing to lock up as collateral. This method is less energy-intensive than PoW. Mining Hardware ASIC Miners Application-Specific Integrated Circuit (ASIC) miners are specialized devices designed for mining specific cryptocurrencies. They offer high efficiency and processing power but lack flexibility. GPU Miners Graphics Processing Units (GPUs) are versatile and widely used in mining various cryptocurrencies, especially those resistant to ASIC mining. GPU mining rigs can be assembled using multiple GPUs to enhance computational power. CPU Miners Central Processing Units (CPUs) are less efficient for mining compared to ASICs and GPUs. However, they are still used for mining certain cryptocurrencies that are optimized for CPU mining. Mining Software Mining Pools Mining pools are groups of miners who combine their computational resources to increase the chances of solving cryptographic puzzles. The rewards are then distributed among the pool members based on their contributed processing power. Mining Clients Mining software clients connect miners to the blockchain network or mining pools. Examples include CGMiner, BFGMiner, and EasyMiner, each offering unique features tailored to different hardware and user preferences. Environmental Impact of Crypto Mining The energy consumption of crypto mining, particularly PoW, has raised environmental concerns. Mining operations require significant amounts of electricity, contributing to carbon emissions. Some cryptocurrencies are transitioning to more energy-efficient consensus mechanisms like PoS to mitigate these impacts. Is Crypto Mining Profitable? Return on Investment (ROI) The profitability of crypto mining depends on various factors, including the initial investment in hardware, electricity costs, and the current price of the cryptocurrency being mined. ASIC miners, while efficient, can become obsolete quickly, affecting long-term profitability. Electricity Costs Electricity is a significant cost factor in mining operations. Regions with lower electricity rates can offer more profitable mining opportunities. Some miners use renewable energy sources to reduce costs and environmental impact. Mining Difficulty and Rewards The mining difficulty adjusts periodically to maintain a consistent block creation time. Higher difficulty means more computational power is required, affecting profitability. Additionally, reward rates for mining can fluctuate based on the cryptocurrency's market value and network policies. Conclusion Crypto mining plays a crucial role in maintaining and securing blockchain networks. While it offers opportunities for earning cryptocurrency, it also comes with challenges such as high energy consumption and significant initial investment. As the industry evolves, new technologies and consensus mechanisms may offer more sustainable and profitable mining solutions. By understanding the intricacies of crypto mining, from the hardware and software involved to the economic and environmental considerations, potential miners can make informed decisions about their participation in this dynamic and ever-changing field.
- 0
- 0
- ₹0